Disclosure: We may earn a commission from links on this page. Learn more.
Best Wi-Fi Channel Settings for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz at Home (2026)

Finding the best Wi-Fi channel settings for your home in 2026 is the key to unlocking fast, stable internet. However, if your router is stuck on “Auto,” it’s likely fighting with your neighbors’ networks for space. This risk of signal overlap means slow speeds and random drops are often caused by local interference rather than your actual internet plan.
The real issue is that most users never log into their router to scan for nearby congestion. By sticking with default settings, even high-end hardware ends up stuck on a weak spot: noisy, overcrowded channels that kill performance.
In this guide, we’ll break down the optimal Wi-Fi channel configuration for 2026. You’ll learn exactly which channels to pick for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz to avoid common mistakes, spot interference, and ensure your gaming and streaming stay lag-free.
Key Takeaways
- Auto settings may not optimize your connection due to interference
- Understanding 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz can help you make informed decisions
- Optimal Wi-Fi channel configuration is essential for better speeds
- Identifying channel interference is crucial for performance
- Manual channel selection often yields better results than auto settings
- Apply specific strategies for dual-band channel selection for efficiency
Understanding Wi-Fi Frequency Bands

Learning about the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands can really improve your Wi-Fi. Each band has its own benefits. Knowing the differences helps you pick the right channels for your needs.
Overview of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Bands
The 2.4 GHz band sits roughly between 2.4 GHz and 2.5 GHz and, depending on your region, offers up to 13 or 14 channels. It’s great for big areas because it goes through walls well.
On the other hand, the 5 GHz band covers several blocks of spectrum roughly between 5.1 GHz and 5.8 GHz, with many more non-overlapping channels. This makes it better for places with lots of devices because it can have less interference.
Differences in Coverage and Speed
When comparing 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz channels, their performance is different. The 2.4 GHz band is perfect for covering large areas. It’s less affected by obstacles than higher frequencies, making it good for big homes.
For faster speeds, the 5 GHz band is better. It’s great for streaming and gaming because it offers quicker data rates. Using both bands together gives the best results in different situations.
Why Selecting the Right Wi-Fi Channel Matters

Choosing the right Wi-Fi channel is key for a good internet experience at home. Wi-Fi channel interference can make your network slow and keep dropping. Knowing about different channels and their impact on your connection is vital for better Wi-Fi.
Impact of Channel Interference on Performance
When many devices use the same or nearby channels, it messes with your signal. This can make downloads slow and your connection unstable. By finding and reducing these problems, you can make your network faster and more reliable.
Non-overlapping Channels Explained
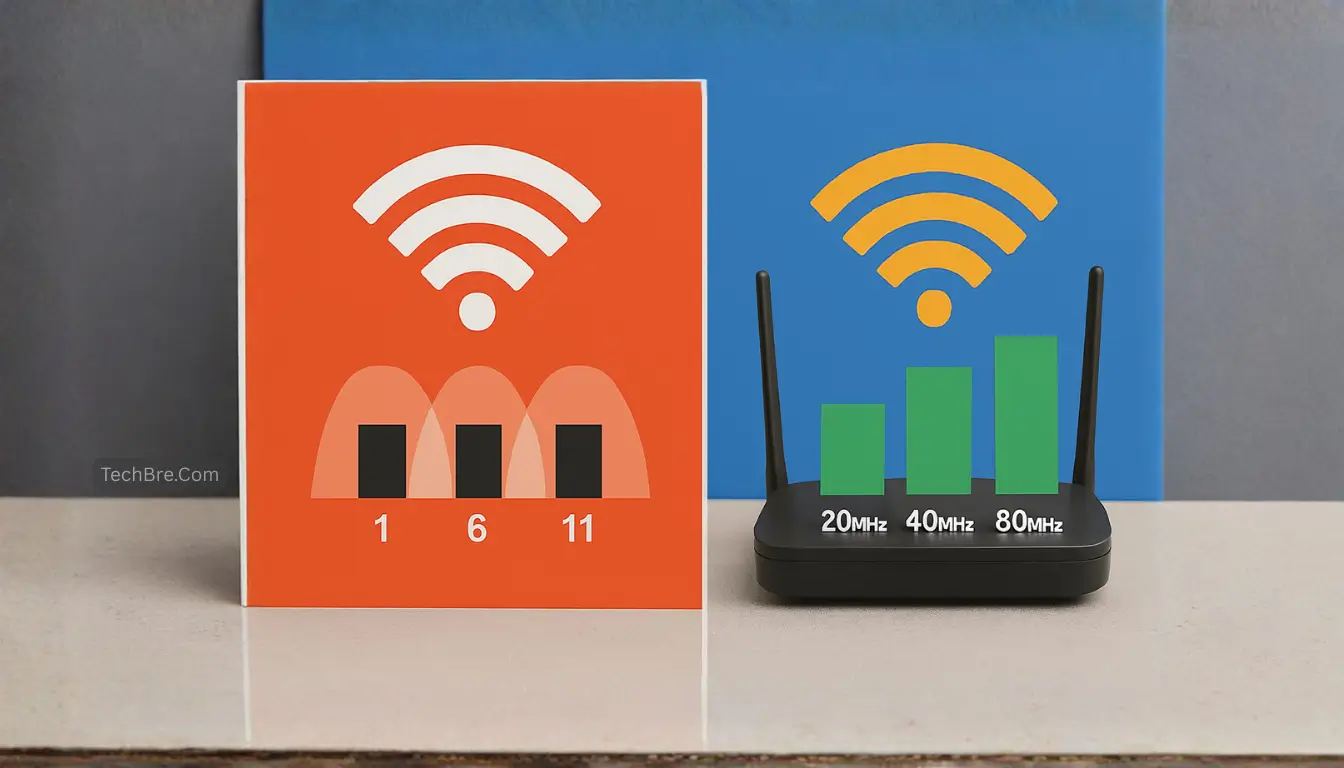
In the 2.4 GHz band, some channels don’t overlap, which is great for less interference. Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the best for this. They help your network run smoother with less congestion. Using these channels can make your home network work better.
Best Wi-Fi Channel Settings for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
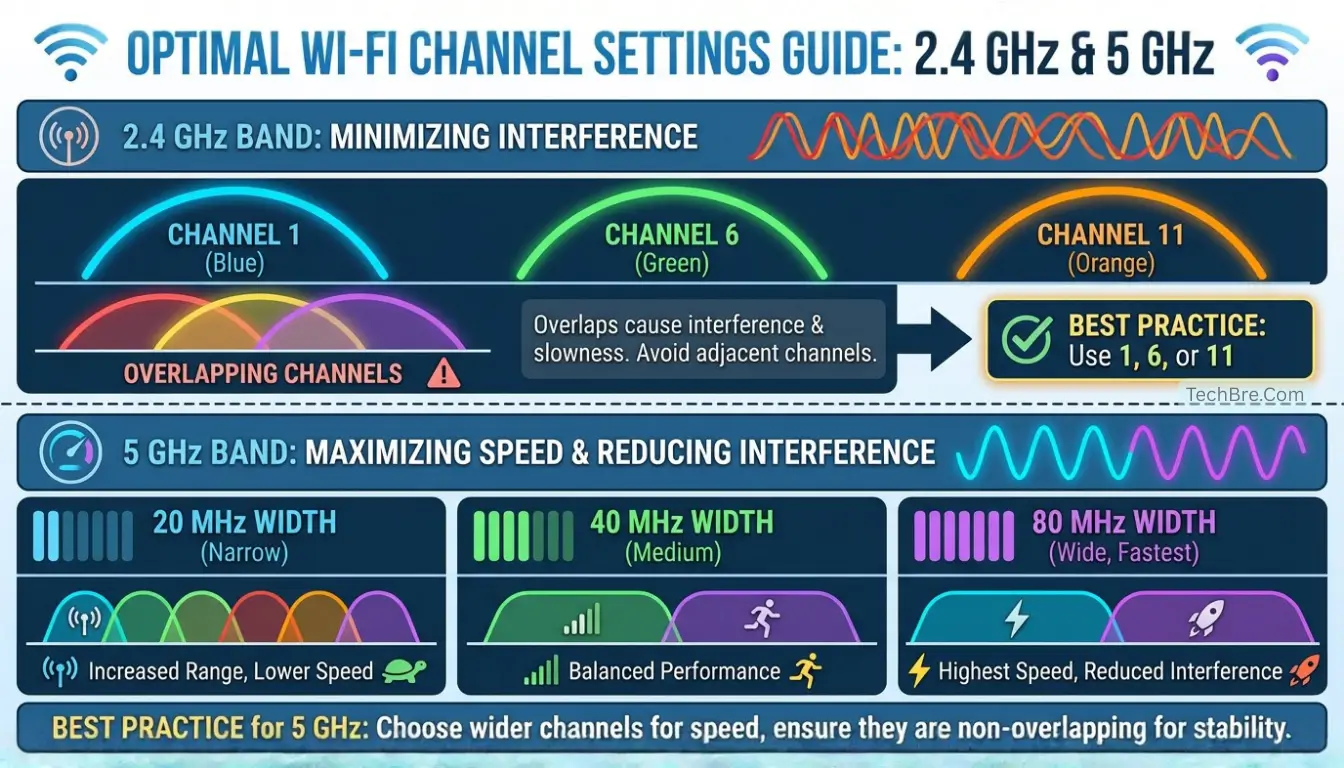
Choosing the right Wi-Fi channel settings can make a big difference at home. Knowing the best settings for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands helps improve your network. This is key for streaming, gaming, and browsing.
Optimal Channels for the 2.4 GHz Band
For the 2.4 GHz band, picking channels with less interference is crucial. The best channels are:
- Channel 1
- Channel 6
- Channel 11
These channels are chosen because they don’t overlap. This reduces interference from other networks. Using these channels keeps your connection stable and fast, even in busy areas.
Recommended Channels for the 5 GHz Band
The 5 GHz band has more channels than the 2.4 GHz band. This means you can use bandwidth more efficiently. Here are the recommended channels for the 5 GHz band:
| Channel | Channel Width | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 36 | 40 MHz | General use |
| 40 | 40 MHz | General use |
| 44 | 40 MHz | Gaming/streaming |
| 48 | 40 MHz | Gaming/streaming |
| 149 | 40 MHz | General use |
| 153 | 40 MHz | General use |
Using a 40 MHz channel width is usually best for speed and less interference in typical home setups. By choosing these channels for the 5 GHz band, you get a strong and efficient connection. This makes online activities smooth and seamless.
Quick Wi-Fi Channel Setup Checklist (2026)
If you want the fastest improvement with the fewest changes, use this simple setup first. You can fine-tune later.
Step 1: Split your bands (if your router allows it)
Give your 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz different names (SSIDs) only if devices keep jumping bands or dropping. If roaming is smooth, keep one name and just set channels manually.
Step 2: Set 2.4 GHz to a clean channel
Use Channel 1, 6, or 11 only. Set channel width to 20 MHz for the most stable performance.
Step 3: Set 5 GHz to a non-DFS channel
Start with 36, 40, 44, or 48. If those are crowded in your area, try 149 or 153 (if available in your country). Use 40 MHz for stability. Use 80 MHz only if your area is quiet.
Step 4: Save, reboot, and test for 5 minutes
After saving settings, reboot the router. Test a video stream and run one speed test in the same room as the router.
Step 5: If it still drops, scan and switch once
Run a Wi-Fi scan (NetSpot/inSSIDer/Wi-Fi Analyzer). Switch to the least busy option from your allowed channels and test again.
Recommended default settings for most homes
| Band | Channel | Width | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz | 1 / 6 / 11 | 20 MHz | Range + smart devices |
| 5 GHz | 36–48 | 40 MHz | Streaming + gaming |
| 5 GHz (backup) | 149 / 153 | 40 MHz | Busy neighborhoods |
Note: Some 5 GHz channels are “DFS” channels. They can be fast, but they may pause or switch if radar is detected. If you want maximum stability, stick to the channels listed above.
Identifying Wi-Fi Channel Interference
To improve your Wi-Fi, first find out what’s causing interference. Knowing where the trouble comes from helps a lot in getting a strong connection.
Common Sources of Interference
Many things can mess with your Wi-Fi. Here are some big offenders:
- Microwave ovens: They use similar frequencies to 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, causing problems.
- Cordless phones: Old models, in particular, can interfere, just like microwaves.
- Neighboring Wi-Fi networks: Routers nearby can cause big issues if they’re on the same channel.
- Bluetooth devices: Bluetooth uses the same frequency as 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi, leading to signal loss.
How to Detect Interference
To spot Wi-Fi interference, you need special tools. Programs like NetSpot or inSSIDer help see what’s going on. Here’s how to use them:
- Scan your area: Run a detailed scan with the software to find out which channels are busy.
- Analyze results: Look at which channels are most used and find out what’s causing trouble.
- Adjust your channel settings: Pick a less crowded channel based on your findings to boost your network.
Understanding where interference comes from and using the right tools makes fixing it easier. This leads to a more stable internet connection.
Optimizing Your Wi-Fi Channel Settings
To get the best network speed, you need to tweak your Wi-Fi channel settings. You can do this by accessing your router’s settings panel. Just type your router’s IP address in your browser to get started. Then, you can adjust channels for better performance in the router settings.
Using Router Settings to Adjust Channels
In the router settings, find the wireless configuration section. There, you can pick a channel manually. The 2.4 GHz band has channels 1 to 11 (in many regions), while 5 GHz has more options. Picking less busy channels can cut down on interference and boost your speed.
Automating Channel Selection for Better Performance
Many routers today have a feature for automatic channel switching. This lets your router change channels on its own based on network conditions. Turning this on makes things easier by adjusting to interference and optimizing your Wi-Fi settings for you.
If your channels are set correctly but smart plugs, cameras, or speakers still drop offline, use this quick fix guide: How to stop smart home devices disconnecting from Wi-Fi.
Advanced Wi-Fi Channel Planning
Effective advanced Wi-Fi channel planning means understanding channel width and choosing the right mixed modes for dual-band routers. Knowing the different channel widths helps you improve your network’s performance. This is based on your environment and the devices you use.
Understanding Channel Width and Its Effects
Channel width greatly impacts your Wi-Fi speed. You have options like 20 MHz, 40 MHz, and 80 MHz. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks.
Using a narrower channel, like 20 MHz, can cut down on interference in busy areas. On the other hand, a wider channel, such as 40 MHz, can increase speeds in less crowded spaces.
Choosing the Best Mixed Mode for Dual-Band Routers
Setting up dual-band routers requires finding the best mixed mode settings. These settings help devices on different bands communicate well. A good mixed mode ensures both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band devices work well together without interference.
If you’re deciding between a single router upgrade and a full mesh system, start here: Routers & Mesh Wi-Fi guides on BreSmartHome.
Conclusion
Choosing the right Wi-Fi channels for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz is key to better internet at home. Knowing how each band works helps you make your Wi-Fi faster and more reliable. This way, you can enjoy things like video calls, streaming, and gaming without interruptions.
Using the best channel settings can make your online activities smoother. It cuts down on lag and keeps your connection stable. Also, reducing interference helps your network work better, even with many devices connected.
By following these tips, you’ll make managing your network easier. You’ll keep your internet running smoothly, now and in the future. Choosing the right channels for your network means you can enjoy a seamless digital life. It’s worth the effort to optimize your Wi-Fi settings.
FAQs
Q: What is the best 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi channel?
A: Channels 1, 6, and 11 are the top choices for the 2.4 GHz band. They don’t overlap and cut down on interference.
Q: What is the best 5 GHz Wi-Fi channel?
A: The 5 GHz band has many non-overlapping channels. Using a 40 MHz channel width can boost performance. But, the best channel for you might depend on local interference.
Q: How can I detect Wi-Fi channel interference?
A: Tools like NetSpot or Wi-Fi Analyzer can help. They scan for interference and show which channels are busy nearby.
Q: How do I optimize my Wi-Fi channel settings?
A: Go to your router’s settings panel. There, you can pick channels manually or use an auto-select feature. This helps based on your network’s conditions.
Q: What role does channel width play in Wi-Fi performance?
A: Channel width impacts your network speed. In crowded areas, a 20 MHz width is best to avoid overlap. For less busy areas, a 40 MHz width can increase speed.
Q: Can I use both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz channels simultaneously?
A: Yes, dual-band routers let you use both bands at once. This helps spread out devices and can improve network performance.
Q: What should I consider when choosing channels for my home network?
A: Think about the interference in your area and how far your devices are from the router. Also, consider what your devices need, like streaming or gaming.
Q: How often should I check my Wi-Fi channel settings?
A: It’s a good idea to check your Wi-Fi channels regularly, especially if you have connectivity problems. Changes in nearby networks can affect your performance.
Further Reading
- How to Find the Best Wi-Fi Channels for Your Router
- Fix Slow 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi at Home (2026 Guide)
- 2.4 GHz vs 5 GHz Wi-Fi: Which Should You Use?
- Windows 11 24H2 Wi-Fi Keeps Disconnecting
- How to Set Up a Guest Wi-Fi Network at Home in 2026
- How to Set Up Mesh Wi-Fi for a Smart Home
- Best Routers for Smart Homes in 2026
For more step-by-step networking tutorials, including mesh setup and router settings, explore Networking & Wi-Fi.








